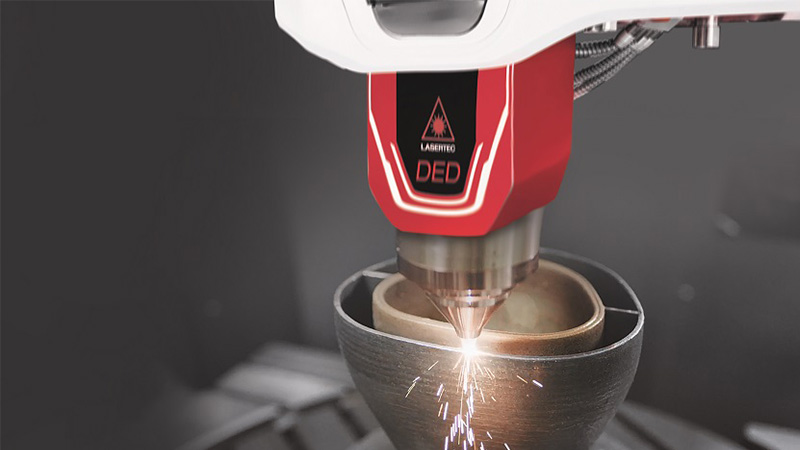
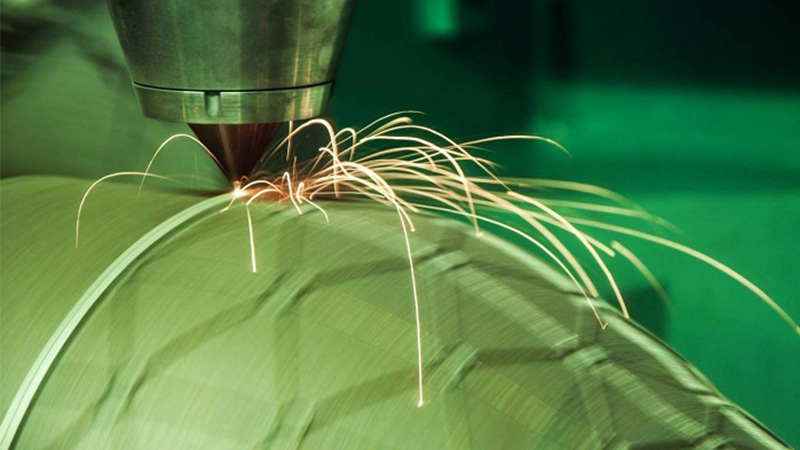
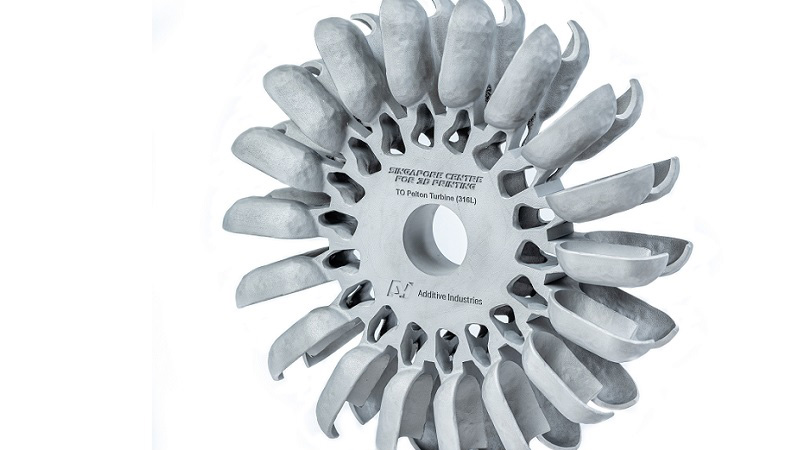
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is disrupting the world of manufacturing in unprecedented ways. The versatile technology lends itself to a diverse range of applications that has driven demand across the globe in the biomedical, construction, and electronics industries, among others.
At JTC’s Jurong Innovation District (JID), Asia’s hub for advanced manufacturing, a growing number of industry leaders in 3D printing are showcasing their capabilities and collaborating with businesses to spur adoption of the technology across the innovation ecosystem.
As SMEs and MNCs tap into the expertise and resources of this community, they forge valuable partnerships and gain the know-how required to adopt new digital solutions in their manufacturing processes. Here is a look at six industry heavyweights in JID leading the charge in the realm of 3D printing.
1. Siemens – First-of-its-kind advanced manufacturing competence centre
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Siemens demonstrated the versatility of 3D printing by solving unexpected challenges. When a hospital in Singapore faced a shortage of face shields, Siemens was able to meet the demand while improving the face shield design for greater comfort and sustainability. In just over a month, Siemens repurposed their production line, increasing the monthly output from 200 to 3,000.
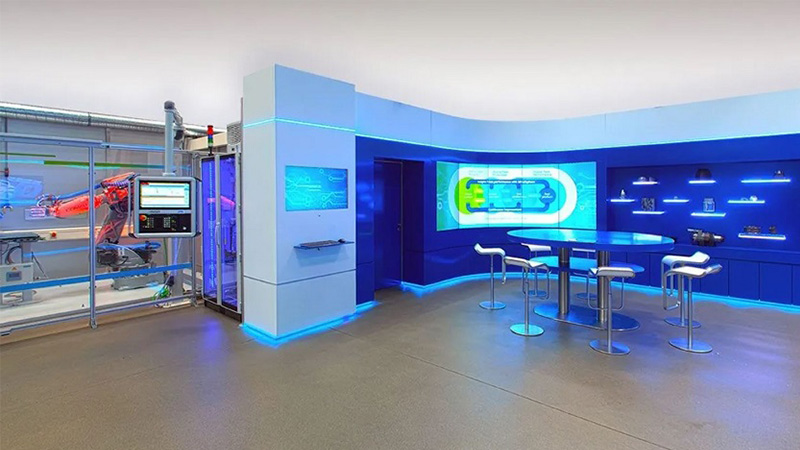
To train businesses in digital adoption by collaborating with technology partners along the value chain, Siemens will launch their first Advance Manufacturing Transformation Centre (AMTC) outside of Germany in JID. Housed within it is an Additive Manufacturing Experience Centre (AMEC), which bridges the gap between 3D printing research and commercialisation by allowing companies to carry out prototyping, supported by on-site experts, as well as workshops and seminars.
Siemens also offers seamless software and automation solutions for 3D printing. With their Digital Enterprise Suite, designers can leverage an end-to-end process chain that extends from design and development to data preparation for components for 3D printing.